Lib & DLL
静态库(Static Library) .lib, 静态链接库比较简单
- 创建静态库项目,可以通过Static Library项目模板,也可以通过Windows Desktop Wizard项目模板创建。
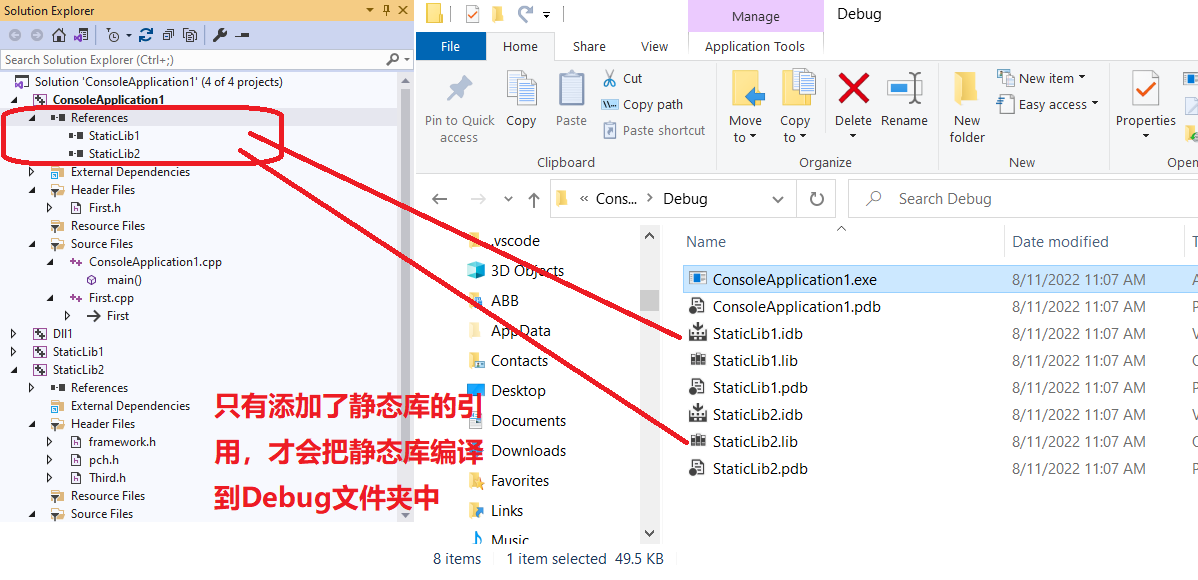
- 创建常规项目,右击References,引用静态库项目,如果不引用,只要使用了静态库中的函数,就会报错。只有引用了静态库,才会自动编译引用的静态库到Debug文件夹中。
-
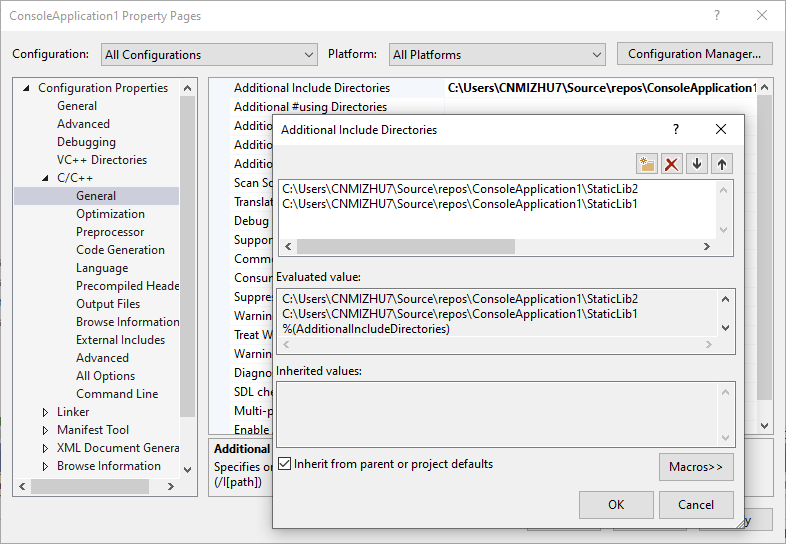
右击项目属性页,设置为“所有配置”,“所有平台”,在”Configuration Properties” -> “C/C++” -> “General” -> “Additional Include Directories”中指定静态库的头文件目录。如果不设置额外的头文件引用路径,那么在引用头文件时,就需要设置相对路径或绝对路径,而不能只设置头文件名。
#include <iostream> #include "First.h" #include "../StaticLib1/Second.h" #include "../StaticLib2/Third.h"
//#include “Second.h” //#include “Third.h”
- 在代码中引用静态库头文件,使用静态库的函数
- 编译常规项目会自动编译静态库项目。
- 程序运行时,不需要静态库
动态链接库(Dynamic-Link Library) .dll
与静态链接库不同的是,Windows 在加载时或在运行时将应用中的导入连接到 DLL 中的导出,而不是在链接时连接它们。 Windows 需要不属于标准 C++ 编译模型的额外信息才能建立这些连接。 MSVC 编译器实现了一些 Microsoft 专用 C++ 扩展,以提供此额外信息。动态链接就是把调用的函数所在文件模块(DLL)和调用函数在文件中的位置等信息链接进目标程序,程序运行的时候再从DLL中寻找相应函数代码,因此需要相应DLL文件的支持。
- 创建动态链接库项目,可以通过Dynamic-Link Library项目模板,也可以通过Windows Desktop Wizard项目模板创建。
- 动态链接库项目的头文件比较特殊
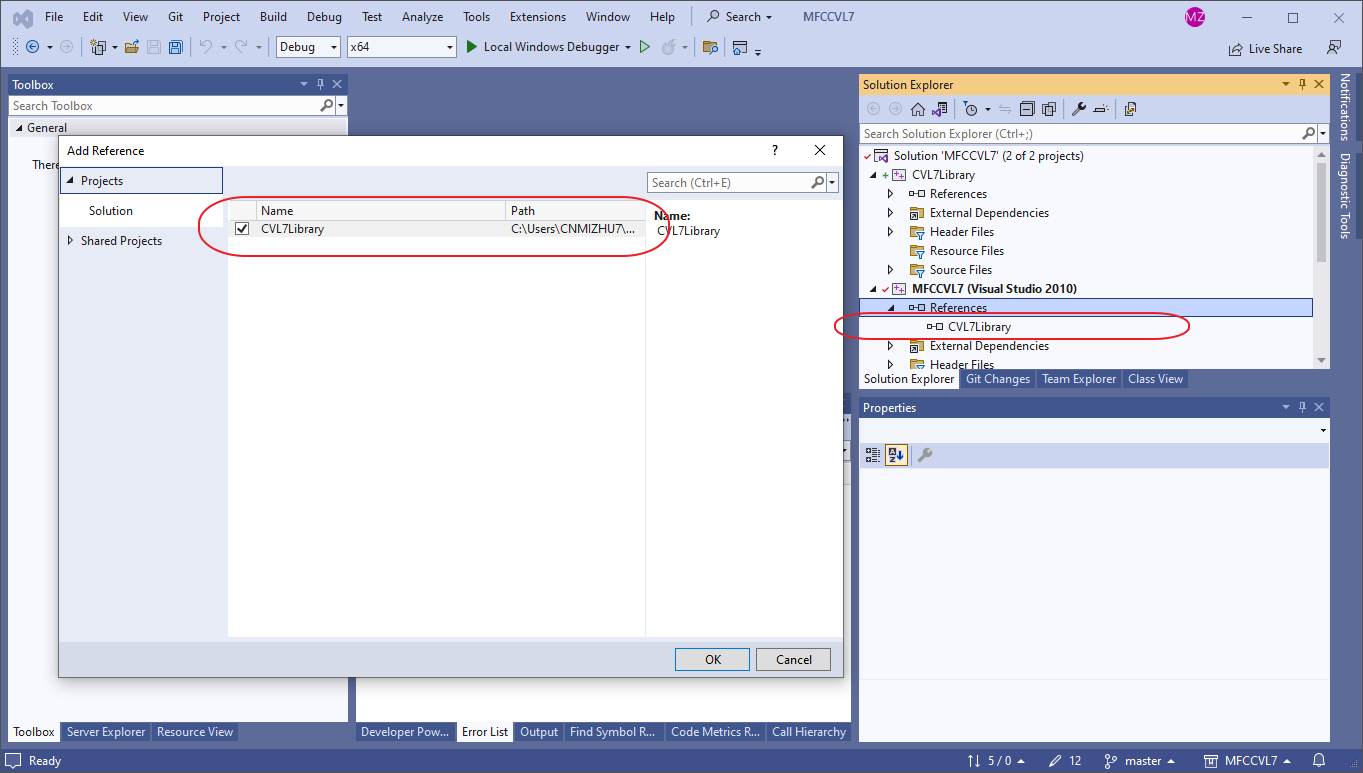
- 创建常规项目,可以不引用动态链接库,但是如果添加引用动态链接库会自动编译动态链接库,否则需要手动编译动态链接库,并确保生成的dll和主程序在同一个目录。如果使用Visual Studio的Add Reference功能引用同一个解决方案下的动态链接库项目,那么可以不需要在主项目中添加lib文件名和文件目录。推荐使用该方法,因为该方法会自动编译依赖的引用dll项目。
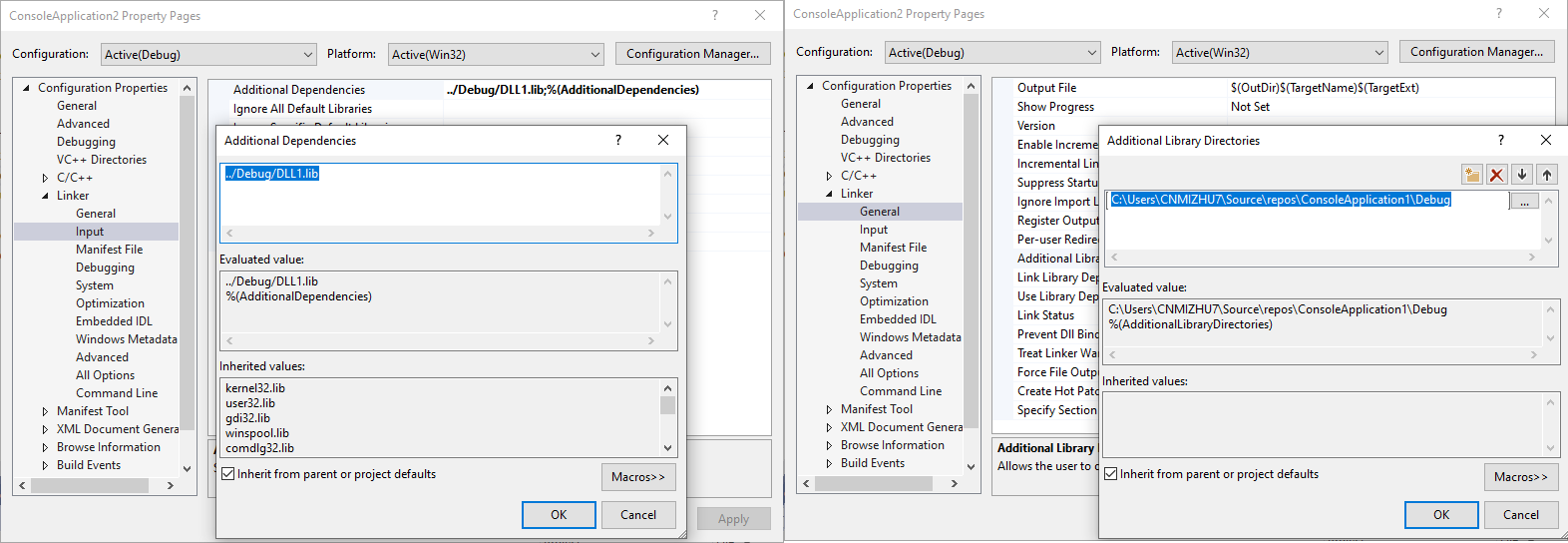
- 右击项目属性页,设置为“所有配置”,“所有平台”,在”Configuration Properties” -> “Linker” -> “Input” -> “Additional Dependencies”中添加动态链接库的lib文件名(非dll文件)。如果使用Visual Studio的Add Reference功能引用同一个解决方案下的动态链接库项目,不需要该操作。
- 在”Configuration Properties” -> “Linker” -> “General” -> “Additional Library Directory”中添加动态链接库的目录,通常为解决方案文件夹下的“Debug”文件夹。可以使用相对路径”..$(IntDir)”,如果在第四步中使用相对地址或绝对地址引用lib文件,那么这边可以不设置附加库目录。如果使用Visual Studio的Add Reference功能引用同一个解决方案下的动态链接库项目,不需要该操作。
- 在代码中引用动态链接库头文件,使用动态链接库的函数,可以使用相对或绝对地址应用,也可以设置额外的头文件引用路径到动态链接库项目文件夹中,此时引用头文件就只需要文件名即可。
- 编译常规项目不会自动编译动态链接库项目,如果在项目中引用了动态链接库项目,则会自动编译,建议引用动态链接库项目。
- 程序运行时,需要动态链接库
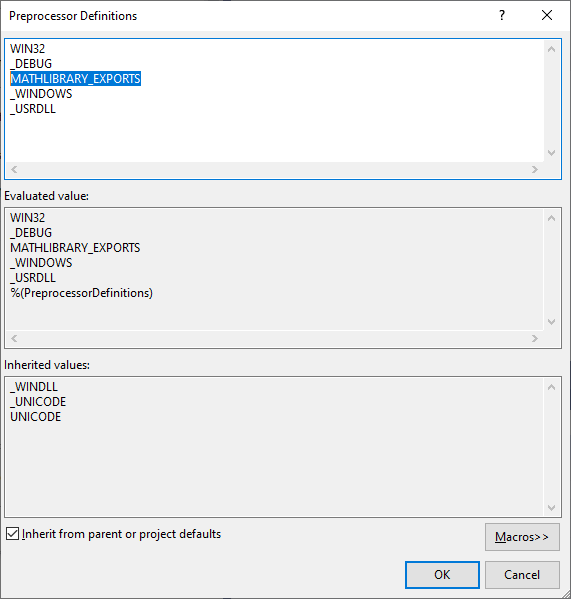
动态链接库预处理指令 dllexport & dllimport
DLL 项目的新项目模板将添加到
When the MATHLIBRARY_EXPORTS macro is defined, the MATHLIBRARY_API macro sets the __declspec(dllexport) modifier on the function declarations. This modifier tells the compiler and linker to export a function or variable from the DLL for use by other applications. When MATHLIBRARY_EXPORTS is undefined, for example, when the header file is included by a client application, MATHLIBRARY_API applies the __declspec(dllimport) modifier to the declarations. This modifier optimizes the import of the function or variable in an application.
// MathLibrary.h - Contains declarations of math functions
#pragma once
#ifdef MATHLIBRARY_EXPORTS
#define DLLAPI __declspec(dllexport)
#else
#define DLLAPI __declspec(dllimport)
#endif
extern "C" DLLAPI void fibonacci_init(const unsigned long long a, const unsigned long long b);
extern "C" DLLAPI bool fibonacci_next();
extern "C" DLLAPI unsigned long long fibonacci_current();
extern "C" DLLAPI unsigned fibonacci_index();
class DLLAPI TestClass
{
public :
int i;
int Sum(int n) { return n + n; }
};
主程序
如果在DLL项目中的预编译头文件stdafx.h中定义DLLAPI,那么有可能头文件中是没有引用stdafx.h预编译头文件,虽然在DLL项目中,编译器会自动引用stdafx.h,但是在主程序中不会自动引用DLL项目的stdafx.h,此时主程序识别不了导出符号DLLAPI,就会导致编译报错。可以同时在主程序的预编译头文件中添加如下代码,这样就可以消除这个编译错误了。
#define DLLAPI __declspec(dllimport)
extern “C”
extern “C”的意思就是用C的方式来导出函数,为什么要用C的方式来导出呢. 因为C++中有重载,编译器会对函数名进行更改,修饰成唯一的函数名.
__declspec(dllexport)
- 代码组件在linux下编译,提供 .so,则在public头文件中的对外函数声明上,无需加 关键字去修饰,因为linux下的动态库接口全是对外开放的;
-
代码组件在windows下编译,提供 .dll, 则要在public头文件中的函数声明上,加上EXPORT关键字,表明该接口是对外可被调用的;
#define EXPORT __declspec(dllexport)
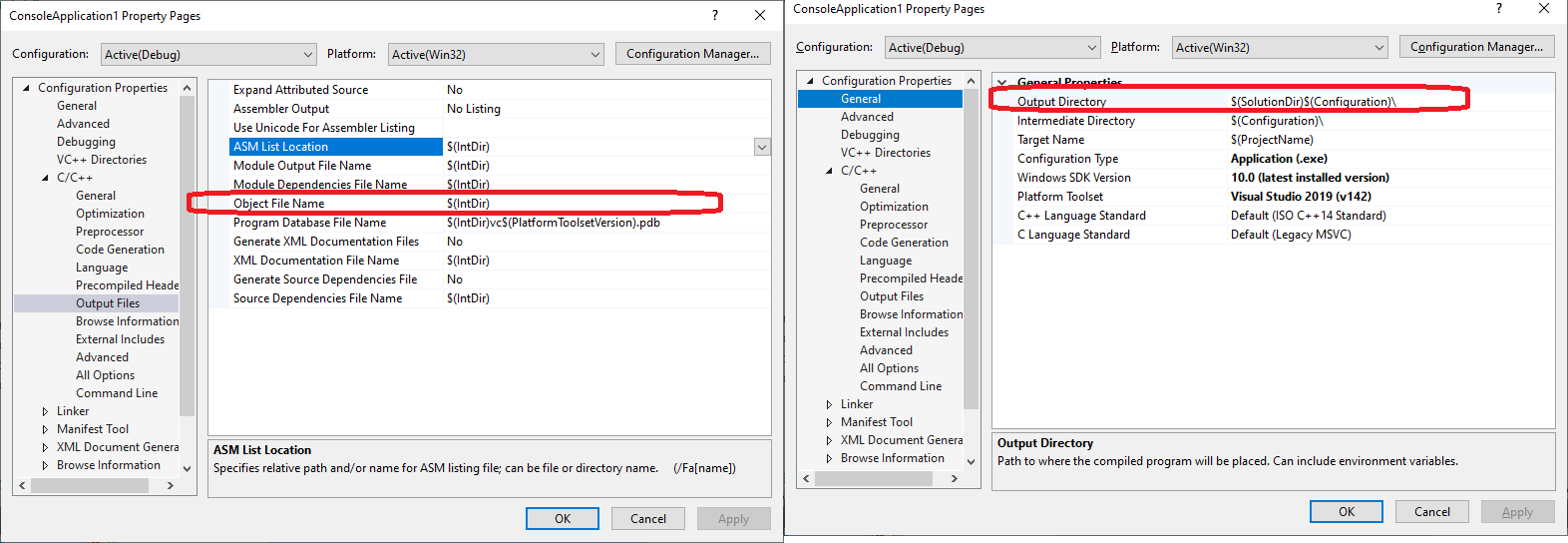
编译生成的目录
- 程序或库目录:$(SolutionDir)$(Configuration)\ = C:\Users\CNMIZHU7\Source\repos\ConsoleApplication1\Debug\
- Intermediate Directory: $(Configuration)\ = Debug\
- obj文件目录:$(IntDir) = Debug\
Include目录和lib目录
编写C++程序时,由两个重要的引用目录:
- 附加头文件目录:Additional Include Directories,当使用第三方库时,需要把该库的头文件目录添加进来,否则在程序中include时,需要使用相对或绝对地址,而不能只写头文件名。
- 附加库目录:当使用动态链接库时,需要在编译时指定lib库的位置。如果没设置库目录,也可以在链接器的Input -> Additional Dependencies中指定库的相对或绝对地址。如果设置了库目录,那么只需要输入库名就可以了。
lib和dll
- lib是编译时需要的,dll是运行时需要的。静态链接库只会编译成lib文件,没有dll;动态链接库既有lib,又有dll,其中lib用于编译,dll用于运行。
- 动态链接库引用时,一定要设置lib文件的依赖
References
如果动态链接库或静态链接库与主项目在同一个解决方案中,理论上只需要在主项目的References中添加链接库的引用,就可以编程调试程序了。此时如果需要引用动态或静态链接库的头文件,必须使用相对或绝对地址,不能直接使用头文件名,因为没有设置附加头文件库,直接使用头文件名,编译器并不知道去哪里找头文件。对于动态连接库,也不需要在Linker -> Input -> Additional Dependencies中设置库名,因为C++项目的特点时所有项目都编译包解决方案的Debug文件中,也就意味着主项目程序exe和动态链接库,静态链接库的lib、dll文件都在同一个目录下,程序在编译和运行时,都会自动去同一目录下去寻找这些库文件,所以就自动进行了链接和执行。
External Dependencies
只要在程序中include的头文件,都会在项目的External Dependencies中显示出来,如果删除该头文件,External Dependencies中也会自动移除该头文件。
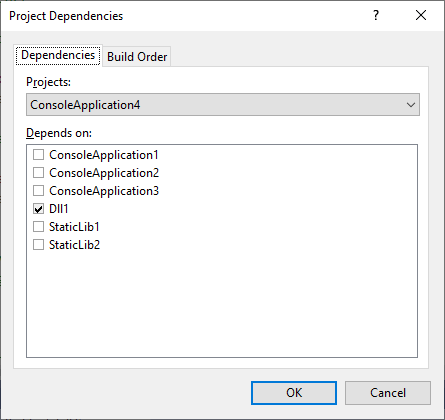
Project Dependencies
通常情况下,如果一个项目引用另一个项目,会在项目依赖中添加关系,且不能删除。如果项目中没有引用关系,又需要强制依赖,那么可以通过右击项目 -> Project Dependencies中设置依赖关系。
查看库函数
-
查看lib文件中函数命令:
dumpbin.exe /LINKERMEMBER dll1.lib > dll1.txt -
查看dll文件中函数命令:
dumpbin.exe /exports dll1.dll > dll2.txt
MFC DLL
通过MFC Dynamic-Link Library创建MFC的动态链接库
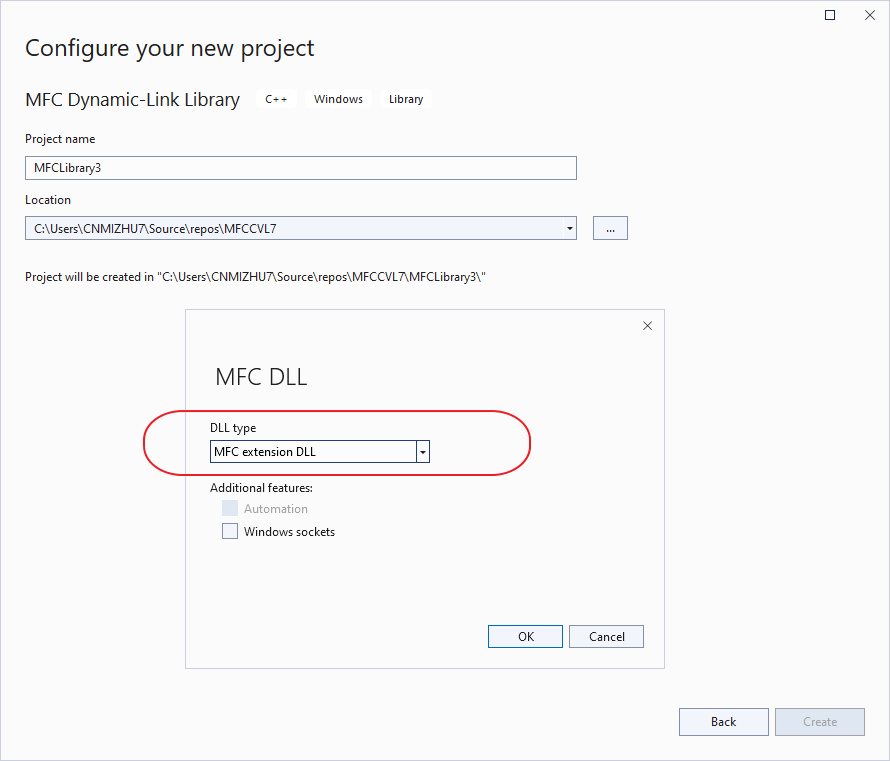
导入库文件
包含lib有两种方式
- 直接在项目属性中的 链接器->输入->附加依赖项 填入lib的路径,此处需要包含lib文件名。
-
在项目属性中的 链接器->常规->附加库目录 填入lib的路径,此处不需要包含lib文件名,然后在调用DLL程序的开头处添加#pragma comment(lib,”XXX.lib”)。
#pragma comment(lib, "XXX.lib")
DllMain
If present, a special function in the DLL, DllMain, is called to do any initialization the DLL requires.
Function’s calling convention.
The programs and the DLL function must be compatible in the following ways:
- The order in which the function expects its arguments to be pushed onto the stack.
- Whether the function or the application is responsible for cleaning up the stack.
- Whether any arguments are passed in registers.
DLL
Unlike a statically linked library, Windows connects the imports in your app to the exports in a DLL at load time or at run time, instead of connecting them at link time.
Windows requires extra information that isn’t part of the standard C++ compilation model to make these connections. The MSVC compiler implements some Microsoft-specific extensions to C++ to provide this extra information.
The DLL uses the C calling convention. It can be called from apps written in other programming languages, as long as the platform, calling conventions, and linking conventions match.
Even though the code of the DLL is written in C++, we’ve used C-style interfaces for the exported functions. There are two main reasons for this: First, many other languages support imports of C-style functions. The client app doesn’t have to be written in C++. Second, it avoids some common pitfalls related to exported classes and member functions. It’s easy to make hard-to-diagnose errors when exporting classes, since everything referred to within a class declaration has to have an instantiation that’s also exported. This restriction applies to DLLs, but not static libraries.
Whether it’s your own or from a third-party, your client app project needs several pieces of information to use a DLL. It needs to find the headers that declare the DLL exports, the import libraries for the linker, and the DLL itself.
To avoid out-of-sync code, we recommend you set the include path in your client project to include the DLL header files directly from your DLL project. Also, set the library path in your client project to include the DLL import libraries from the DLL project. And finally, copy the built DLL from the DLL project into your client build output directory. This step allows your client app to use the same DLL code you build.
you can set the Additional Dependencies property to tell the build system that your project depends on MathLibrary.lib. And, you can set an Additional Library Directories path in your project to include the path to the original library when you link.
Include Directories & Library Directories & Additional Include Directories & Additional Library Directories
C++ Property Pages -> Configuration Properties -> VC++ Directories -> Include Directories 和 Library Directories配置的使系统头文件和系统库文件目录,虽然也可以在这边把第三方库的头文件目录和库文件目录添加进来,但是不建议这么做。第三方库的头文件目录应该在C++ Property Pages -> Configuration Properties -> General -> Additional Include Directories中添加,第三方库的库目录应该在C++ Property Pages -> Configuration Properties -> Linker -> General -> Additional Library Directories中添加。
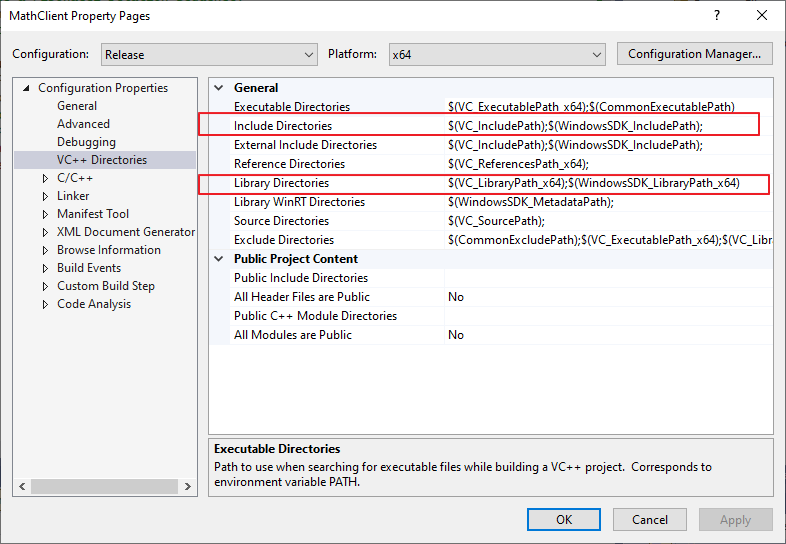
Additional Library Directories & Additional Dependencies
Additional Library Directories设置的是库目录,不代表VS会自动把这个目录的所有库文件都加载到程序中去,只有在Additional Dependencies添加的库文件,才会被加载,库文件的查找位置就是Additional Library Directories设置的目录。
动态加载 LoadLibrary
// DLL1
#ifdef DLL1_EXPORTS
#define DLLAPI __declspec(dllexport)
#else
#define DLLAPI __declspec(dllimport)
#endif
extern "C" DLLAPI int multipy(int n);
typedef int (WINAPI* MY_FUNC)(int);
MY_FUNC func;
DLLAPI int multipy(int n)
{
return n*n;
}
// ConsoleApplication3
#include <iostream>
#include <Windows.h>
#include <tchar.h>
#include "../Dll1/MathLibrary.h"
int main()
{
HMODULE dllHandle1 = LoadLibrary(_T("C:\\Users\\CNMIZHU7\\Source\\repos\\ConsoleApplication3\\x64\\Debug\\Dll1.dll"));
if (NULL == dllHandle1)
{
std::cout << "No Dll!\n";
}
else {
std::cout << "Dll exist!\n";
func = (MY_FUNC)GetProcAddress(dllHandle1, "multipy");
std::cout << func(20) << std::endl;
FreeLibrary(dllHandle1);
}
std::cout << "Hello World!\n";
}
__cplusplus
__cplusplus是什么, __cplusplus是gcc编译器在编译.cpp文件或g++编译器在编译.c/.cpp文件时需要加入的宏定义;这个宏定义标志着编译器会把代码按C++的语法来解释。注意当源文件为cpp文件时,MSVC编译器也会加入这个预定义宏。
- 指定gcc编译 .c文件,__cplusplus没有定义,编译器按照c编译代码
- 指定gcc编译 .cpp文件,__cplusplus有定义,编译器按照c++编译代码
extern “C”
extern “C”的主要作用就是为了能够正确实现C++代码调用其他C语言代码。加上extern “C”后,会指示编译器这部分代码按C语言的进行编译,而不是C++的。由于C++支持函数重载,因此编译器编译函数的过程中会将函数的参数类型也加到编译后的代码中,而不仅仅是函数名;而C语言并不支持函数重载,因此编译C语言代码的函数时不会带上函数的参数类型,一般只包括函数名。
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C"{ //告诉编译器,这部分代码按C语言的格式进行编译,而不是C++的
#endif
/*.................................
* do something here
*.................................
*/
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif