Visual C++ Configuration
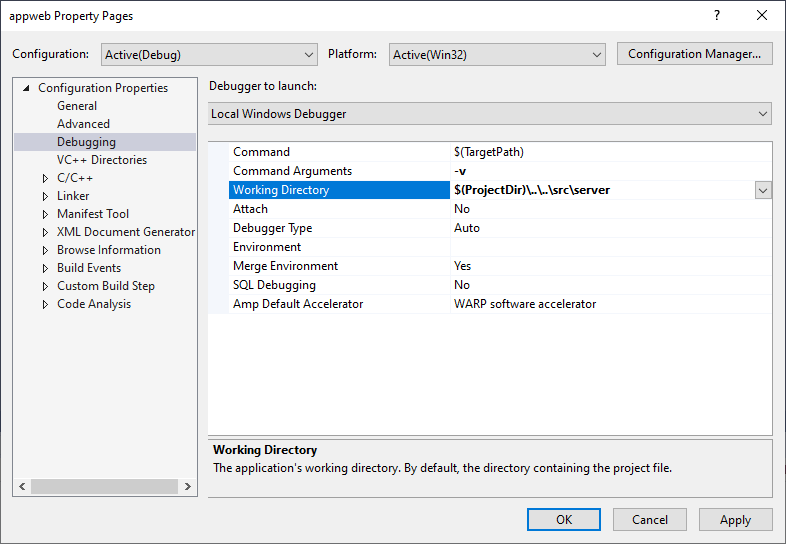
设置项目工作目录和命令行参数
可以通过Configuration Properties -> Debugging -> Working Directory / Command Arguments 设置C++程序运行时的工作目录和命令行参数。
Working Directory: $(OutDir)
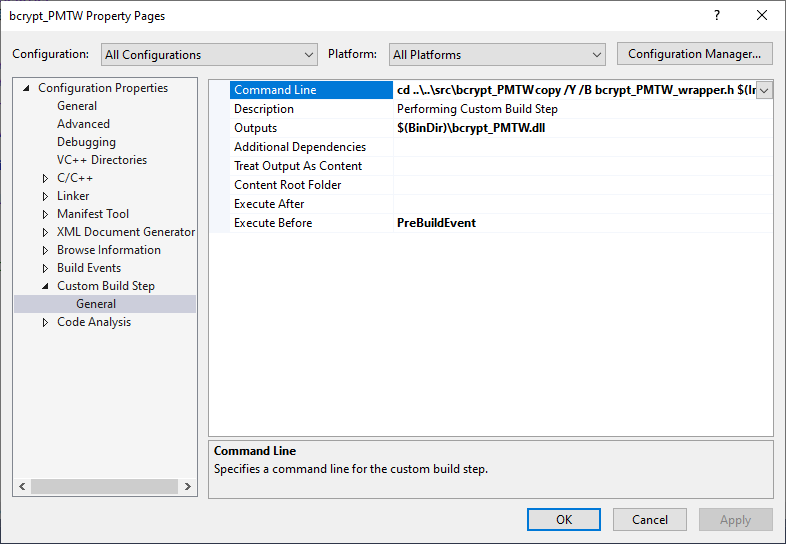
CustomBuildStep
可以设置项目的自定义事件,这样可以在Build时自动运行一些脚本。如可以提前把.h文件复制到某一个文件夹下。Outputs里设置的文件名用于监控是否要运行指令,当该文件没有更新时,就不会运行该指令,只有发现该文件有变化时,才会运行该指令,可以提高编译效率。
cd .
if not exist "$(ObjDir)" md "$(ObjDir)"
if not exist "$(BinDir)" md "$(BinDir)"
if not exist "$(IncDir)" md "$(IncDir)"
if not exist "$(IncDir)\me.h" copy "..\appweb-windows-default-me.h" "$(IncDir)\me.h"
copy /Y /B ..\..\src\appweb.h $(IncDir)
copy /Y /B ..\..\src\server\windows\appwebMonitor.h $(IncDir)
copy /Y /B ..\..\src\customize.h $(IncDir)
copy /Y /B ..\..\src\mbedtls\embedtls.h $(IncDir)
copy /Y /B ..\..\src\esp\esp.h $(IncDir)
copy /Y /B ..\..\src\http\http.h $(IncDir)
copy /Y /B ..\..\src\mbedtls\mbedtls.h $(IncDir)
copy /Y /B ..\..\src\server\windows\monitorResources.h $(IncDir)
copy /Y /B ..\..\src\mpr-version\mpr-version.h $(IncDir)
copy /Y /B ..\..\src\mpr\mpr.h $(IncDir)
copy /Y /B ..\..\src\osdep\osdep.h $(IncDir)
copy /Y /B ..\..\src\pcre\pcre.h $(IncDir)
cd .
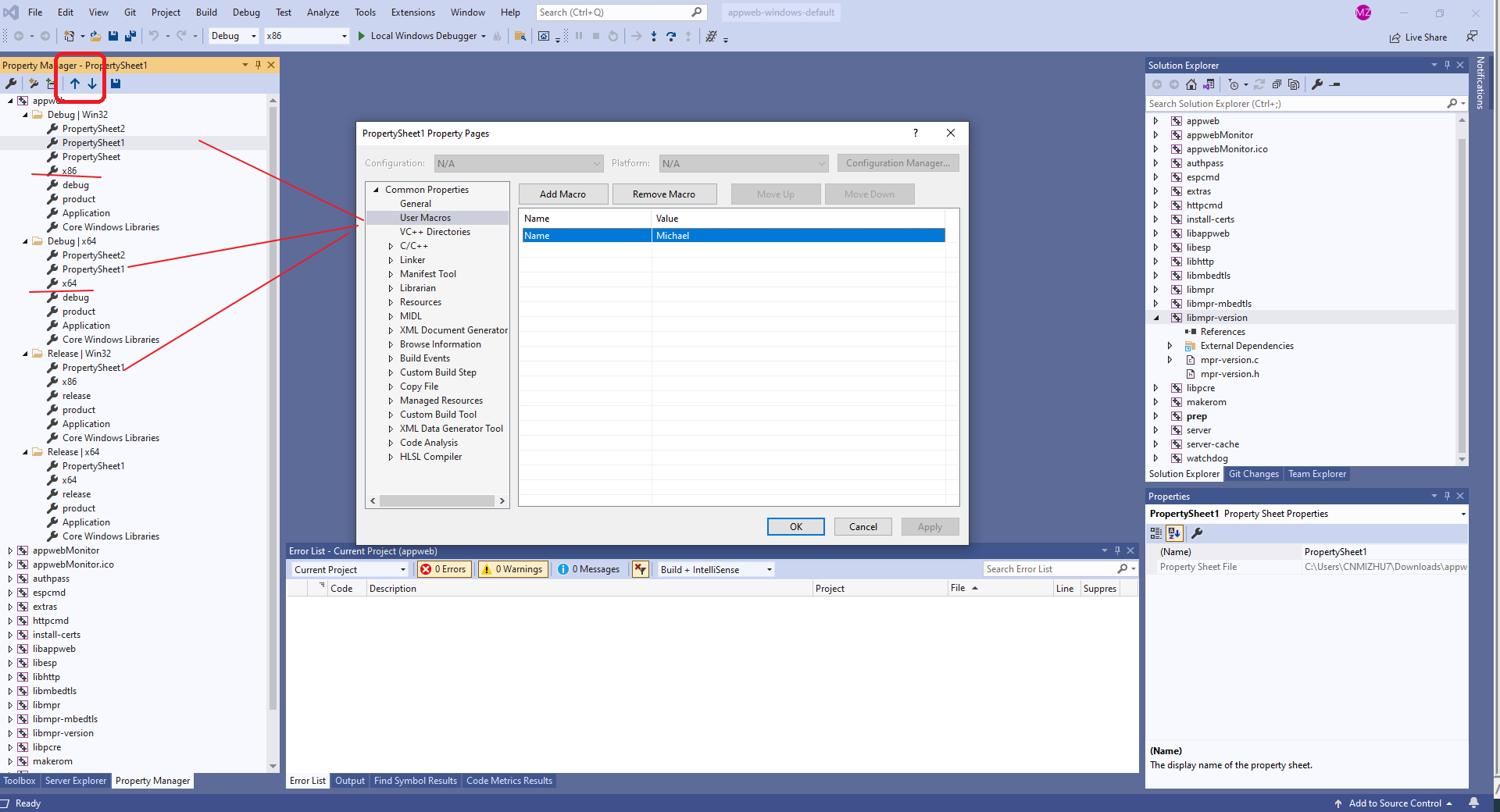
Project Manager
项目中的自定义宏在Project Manager中管理。
- Project Property:又称项目属性,是你当前项目的属性配制,保存在你工程的配制文件中,ProjectName.vcxproj中。
- Property Sheet:又称属性表,可用于多个工程的属性配制,可以自己创建添加属性配制,也可以使用系统默认的属性表,保存在.props为拓展名的文件中。而属性表(Property Sheet)的添加和管理就是在Property Manager中进行设置的。
- Microsoft.Cpp.Win32.user是当 前系统用户默认的属性表,保存在C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Microsoft\MSBuild\v4.0\Microsoft.Cpp.Win32.user.props中
- 项目的属性是分层的。 每一层会继承前一层的值,通过调整顺序在同一层中确认继承关系。
C++的入口函数
我们最开始学习c++时,就知道要写一个main()函数,并且知道这是整个函数的入口,但是c++不只有main()函数这一个入口。对于不同的程序函数入口是不同的。并且,在整个可执行文件执行之前,有一些程序在main()函数之前被执行。
- main()是WINDOWS的控制台程序(32BIT)入口或DOS程序(16BIT)入口。
- WinMain()是WINDOWS的GUI程序入口。
- wmain()是UNICODE版本的main()。
- _tmain()是个宏,如果是UNICODE则他是wmain()否则他是main()。
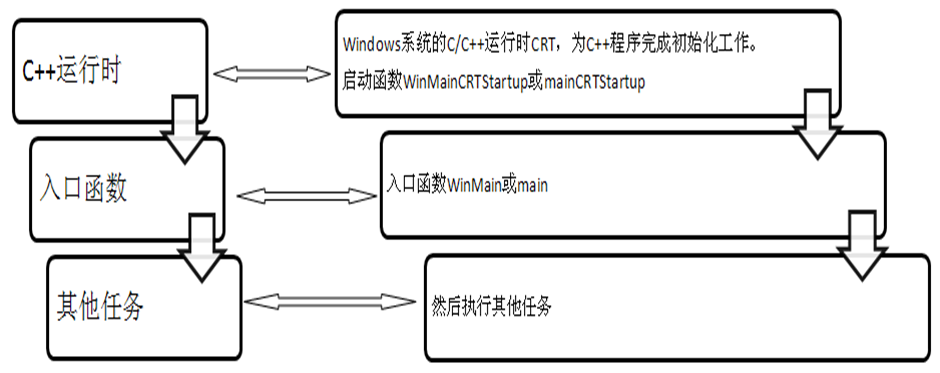
C++程序启动过程
C++程序的启动运行,需要C++运行时环境。C++运行时为C++程序提供必要的运行环境,是先于“main函数”运行的,C++程序第一个被执行的函数会因为C++运行时不同而不同。例如,在Windows操作系统下,C++运行时的启动函数WinMainCRTStartup或mainCRTStartup是第一个被执行的函数。在C++运行时初始化工作完成后,才会调用类似“main”的函数。基于此,一个类似入口点的C++入口函数定义:C++运行时为C++程序提供必要的运行环境;在C++运行时初始化工作完成后,第一个调用的函数是入口函数。其中w开头的函数时unicode版本的。
- mainCRTStartup(或 wmainCRTStartup), 使用 /SUBSYSTEM:CONSOLE 的应用程序
- WinMainCRTStartup(或 wWinMainCRTStartup), 使用 /SUBSYSTEM:WINDOWS 的应用程序
- _DllMainCRTStartup, 调用 DllMain(如果存在),DllMain 必须用 __stdcall 来定义
Windows platforms (CRT)
The C run-time libraries for Visual Studio support all versions of Windows and Windows Server that are still in extended support. Libraries are available for x86, x64, and ARM64. All of these operating systems support the Windows desktop API (Win32) and provide Unicode support. In addition, any Win32 application can use a multibyte character set (MBCS).
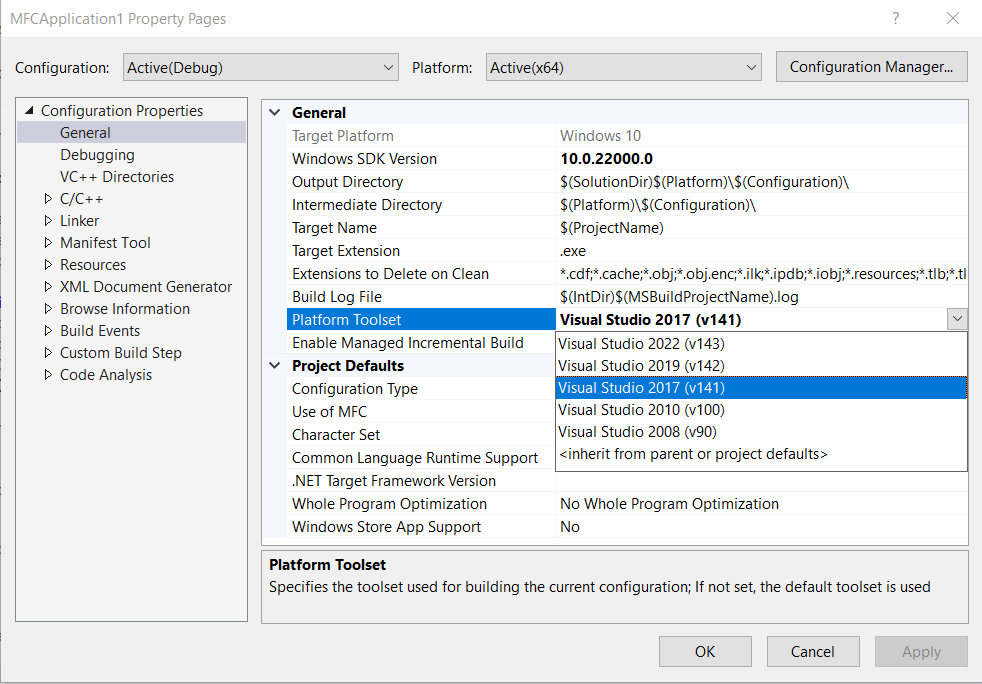
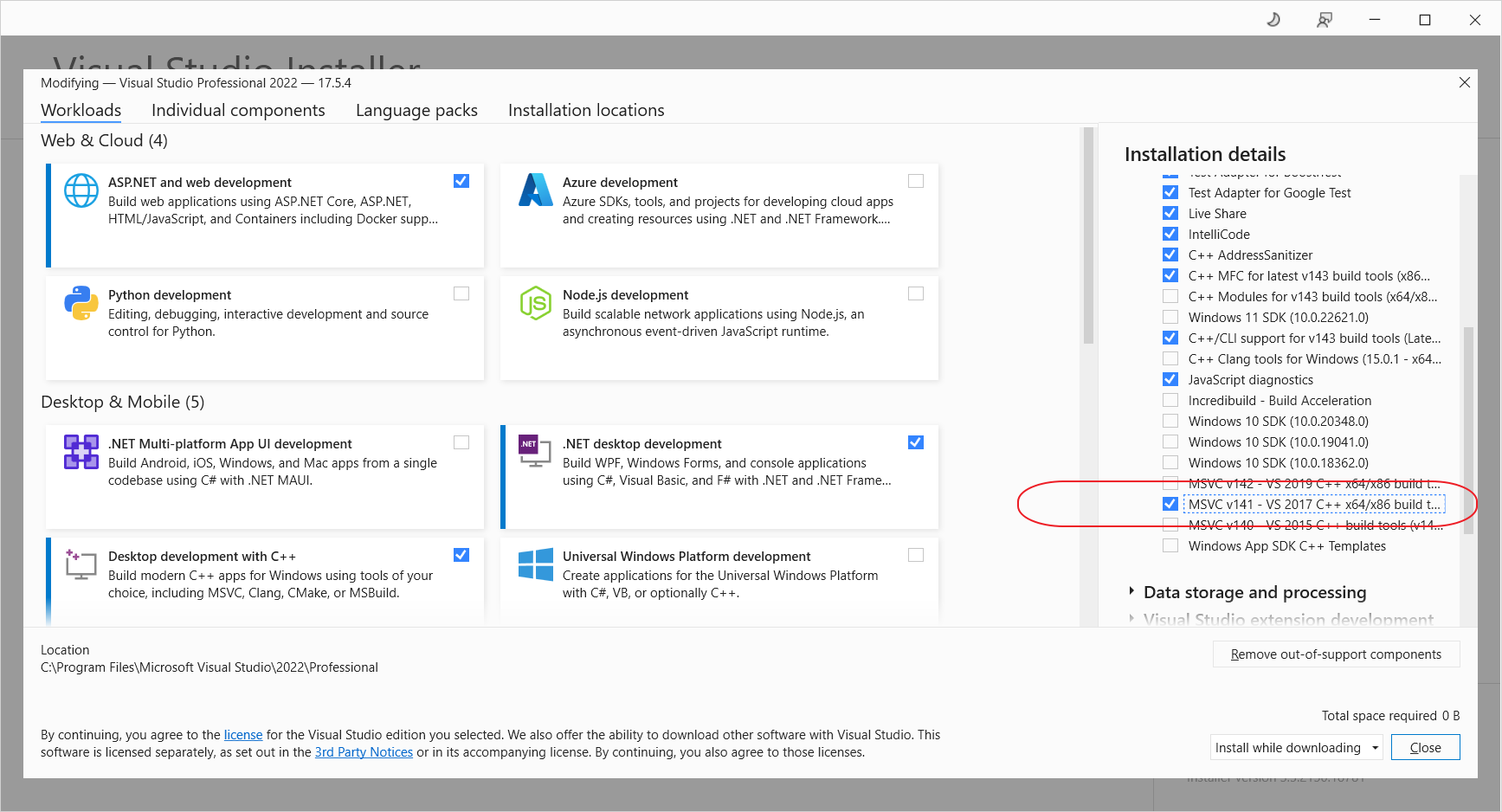
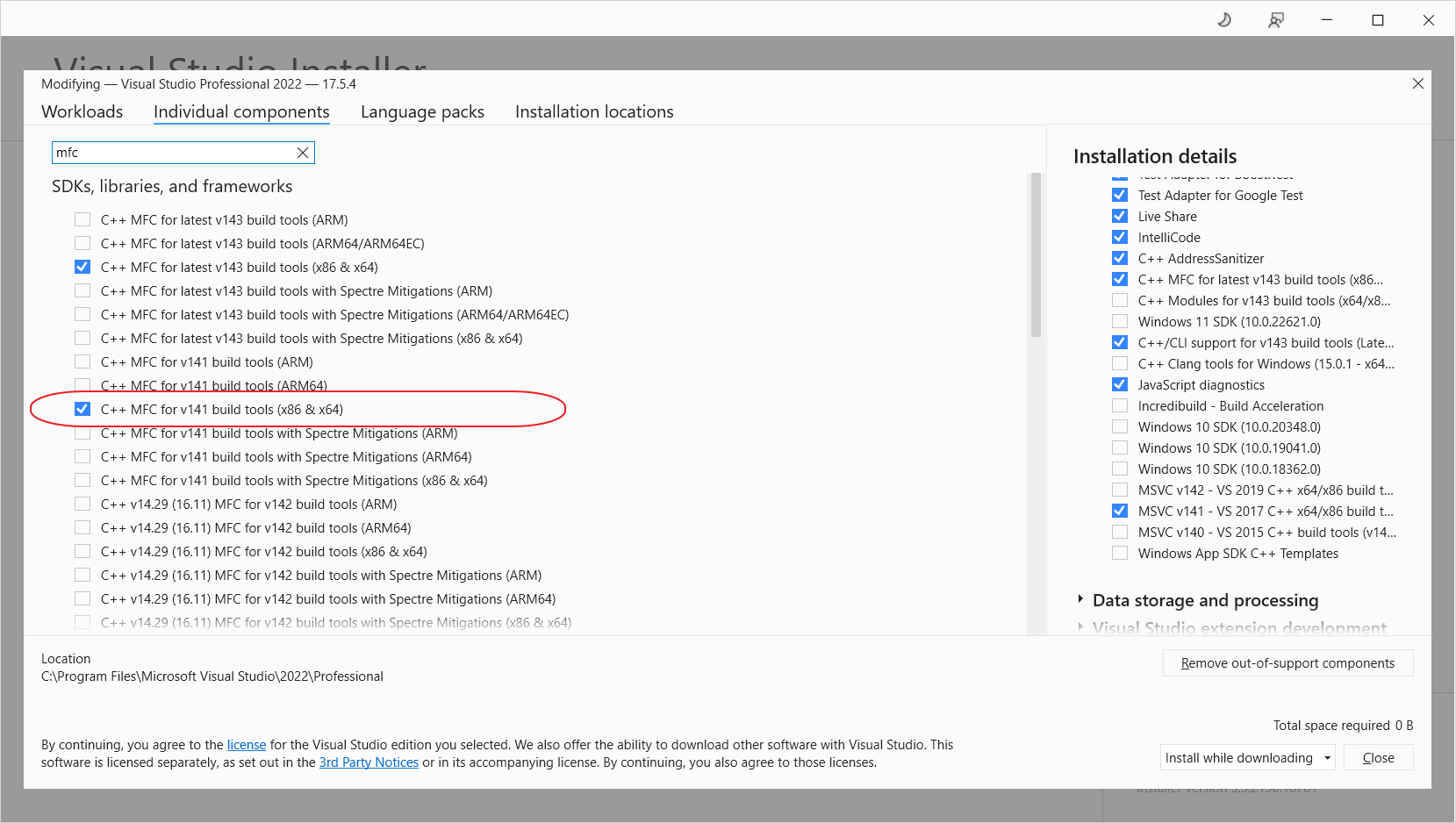
MSVCv141
如果需要Visual Studio 2022支持Visual Studio 2017编译器编译,需要添加MSVC v141 - VS 2017 C++ x86/x64 build tools和 C++ MFC for v141 build tools (x86 & x64)两个选项。
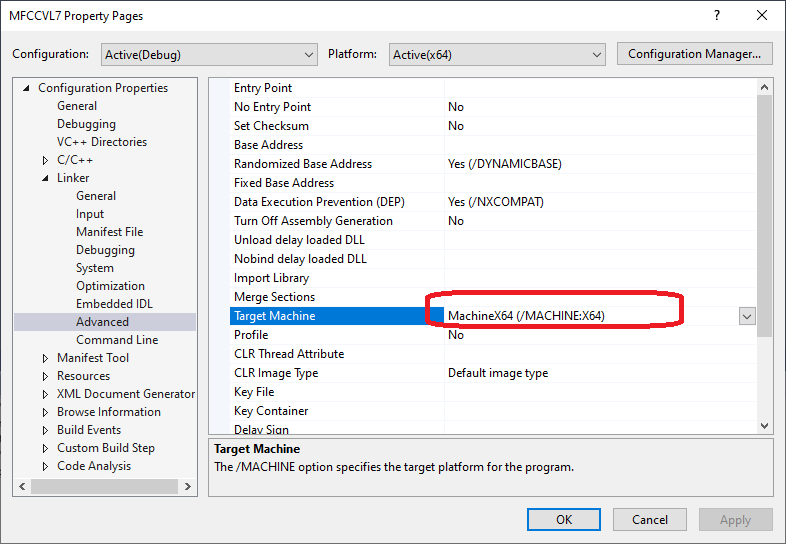
Target Machine
通过修改Configuration Properties -> Linker -> Advanced -> Target Machine = MachineX64,可以把程序编译为64位版本。
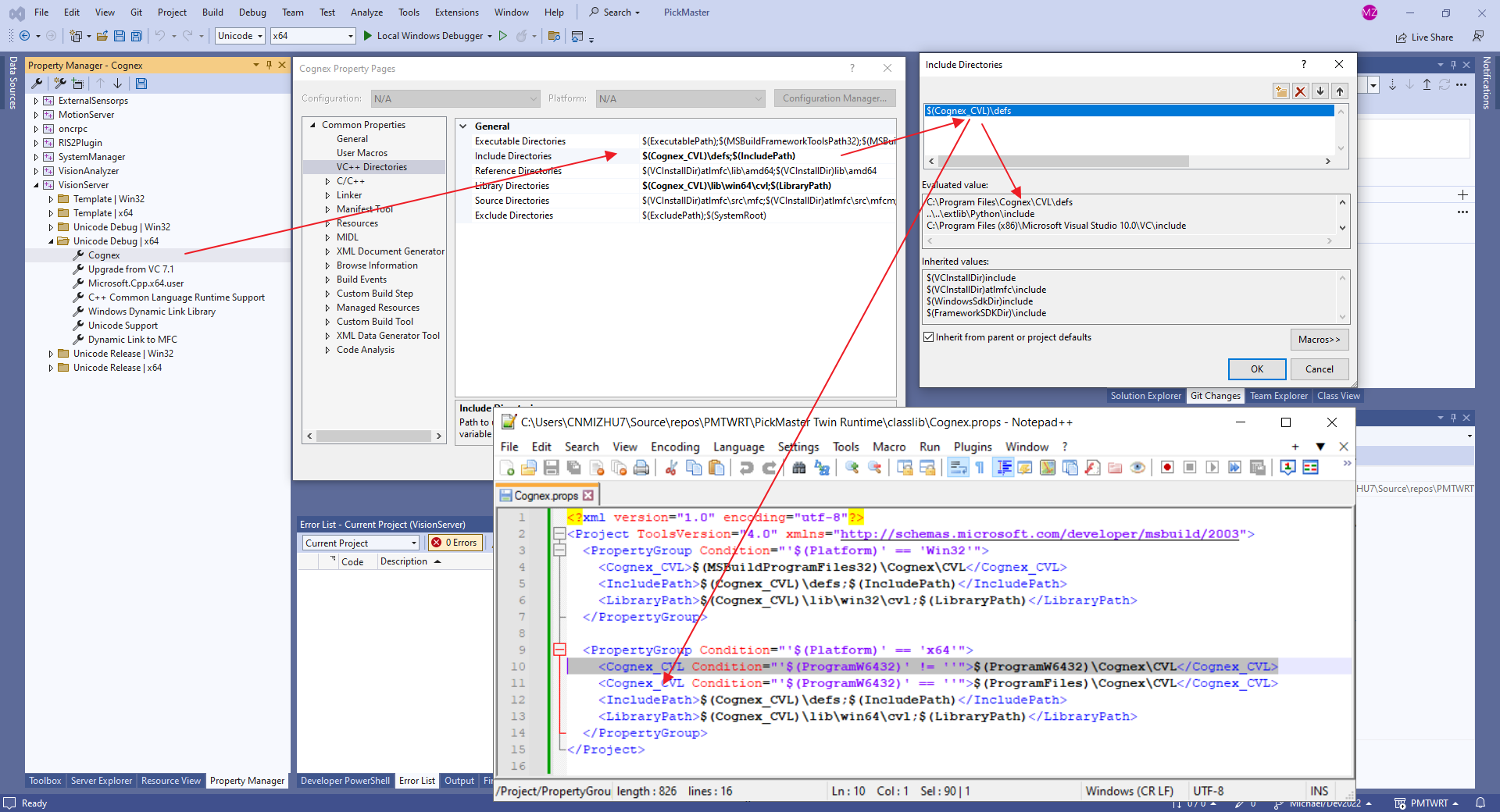
Property Manager Macro
可以在*.props中创建宏变量,然后在配置中引用该变量定义的值。该宏变量可能不能直接用Visual Studio查看,只能手动打开配置文件查看或修改。
重写函数
通过类视图的属性,可以查看Overrides选项卡,选择需要重写的函数,新建,就可以在子类中直接添加重写函数。
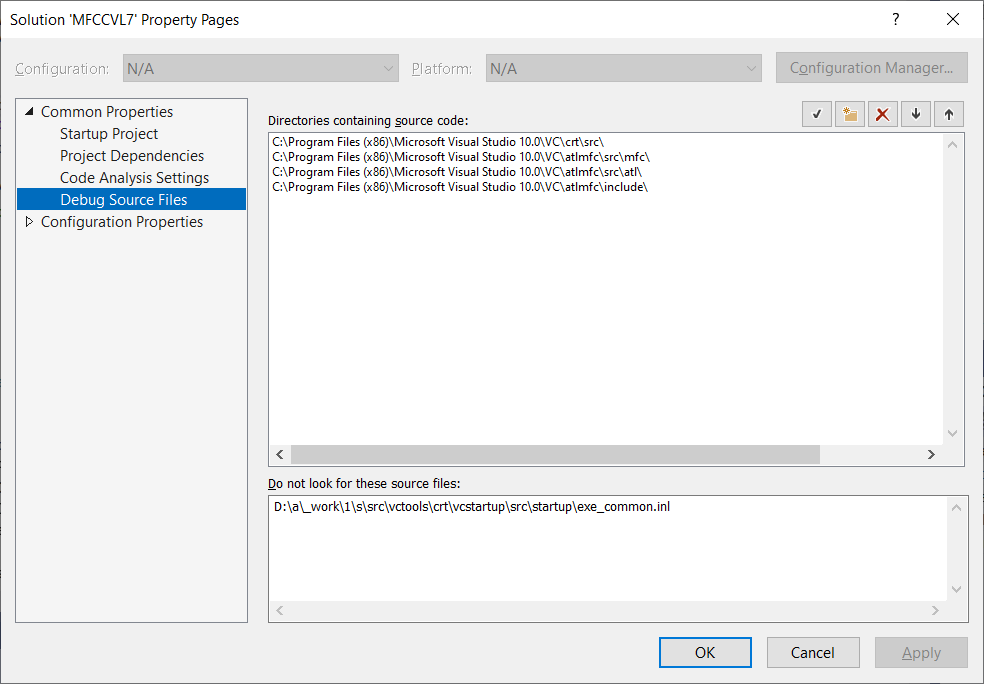
MFC源代码位置
通过Solution Property -> Common Properties -> Debug Source Files可以查看MFC源代码的位置,貌似这个参数存储在.vs\MFCCVL7\v17.suo文件中。不清楚正确的修改方式是什么?该位置会影响把MFC设置为静态库时单步调试代码到MFC源代码时的功能。
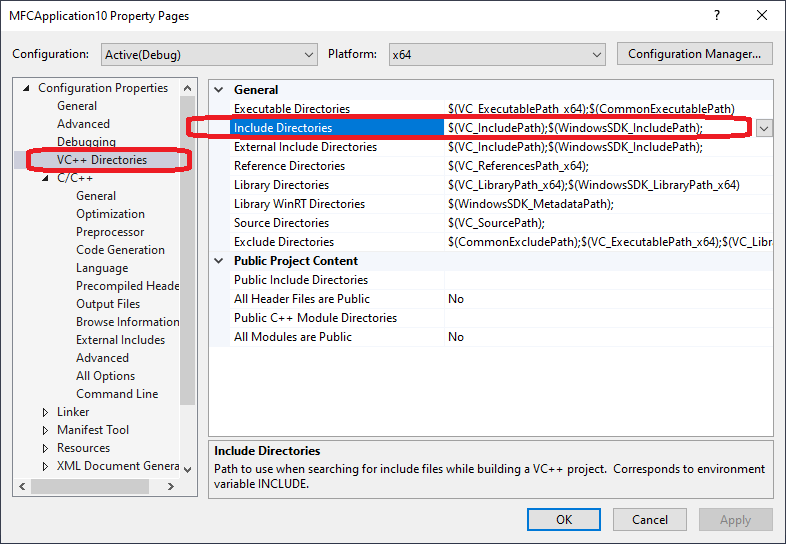
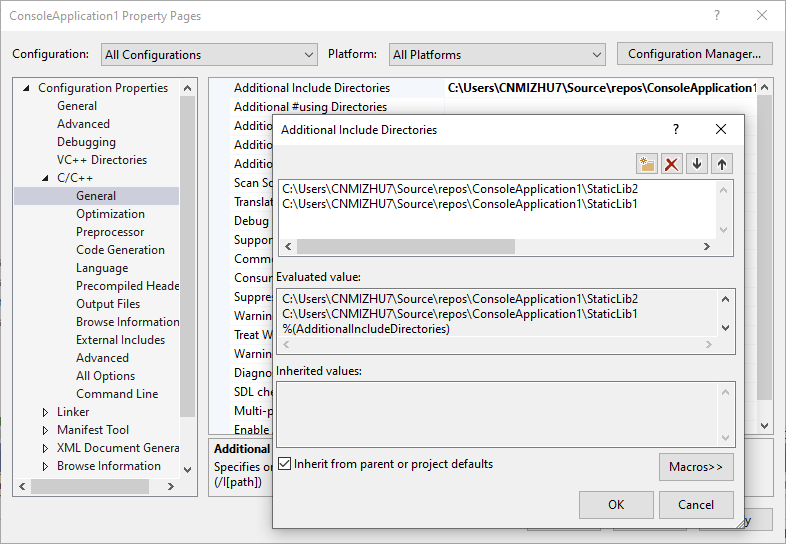
“Include Directories” 和 “Additional Include Directories”
在Visual Studio中有两个地方可以设置第三方库的头文件夹,分别是Project Property -> VC++ Directories -> Include Directories 和 Project Property -> C/C++ -> General -> Additional Include Directories.
The compiler searches for directories in the following order:
- Directories containing the source file.
- Directories specified with the /I option, in the order that CL encounters them. (C/C++ -> General -> Additional Include Directories)
- Directories specified in the INCLUDE environment variable. (VC++ Directories -> Include Directories)
Microsoft.Cpp.x64.user.props & Microsoft.Cpp.Win32.user.props
Microsoft.Cpp..user.props were introduced in VS2010 as a replacement to VS2008’s VC Directories page in Tools - Options and a way to migrate the user options from those releases. VS2019 does not support this conversion anymore and does not create empty Microsoft.Cpp..user.props either. The projects will still import those files in they exist, but we recommend using new ways of defining common properties which allow better control and maintanability.
C:\Users\Michael\AppData\Local\Microsoft\MSBuild\v4.0\Microsoft.Cpp.Win32.user.props
C:\Users\Michael\AppData\Local\Microsoft\MSBuild\v4.0\Microsoft.Cpp.x64.user.props
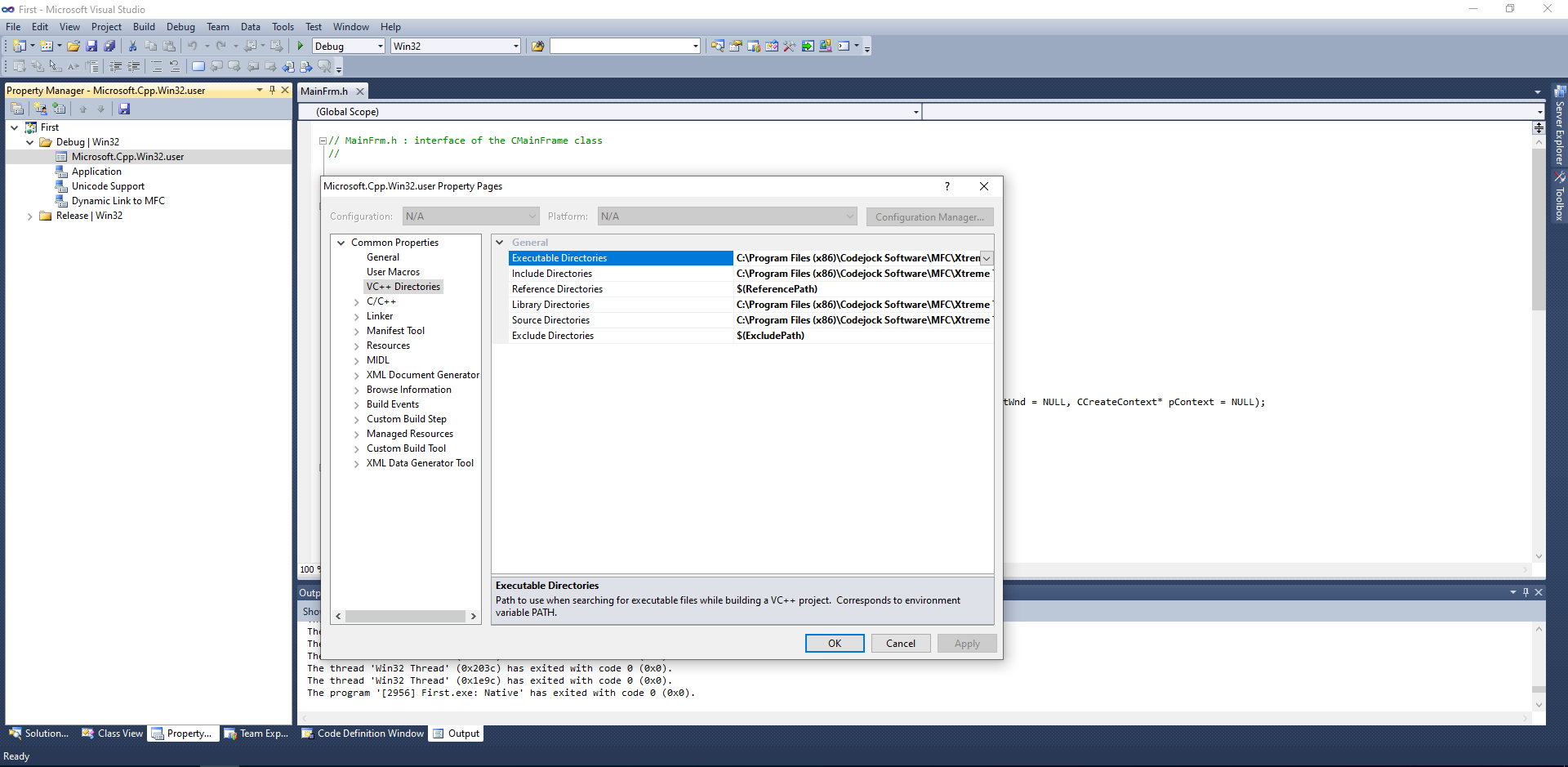
Property Manager
| Name | directory | file | Description | |:———–|:———–|:———–|:———–| | Microsoft.Cpp.Win32.user | %LOCALAPPDATA%\Microsoft\MSBuild\v4.0 | Microsoft.Cpp.Win32.user.props | | | Microsoft.Cpp.Win32.user | %LOCALAPPDATA%\Microsoft\MSBuild\v4.0 | Microsoft.Cpp.x64.user.props | | | Microsoft.Cpp | C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio\2022\Professional\Msbuild\Microsoft\VC\v170 | Microsoft.Cpp.props | | | Microsoft.Cpp.Default | C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio\2022\Professional\Msbuild\Microsoft\VC\v170 | Microsoft.Cpp.Default.props | |
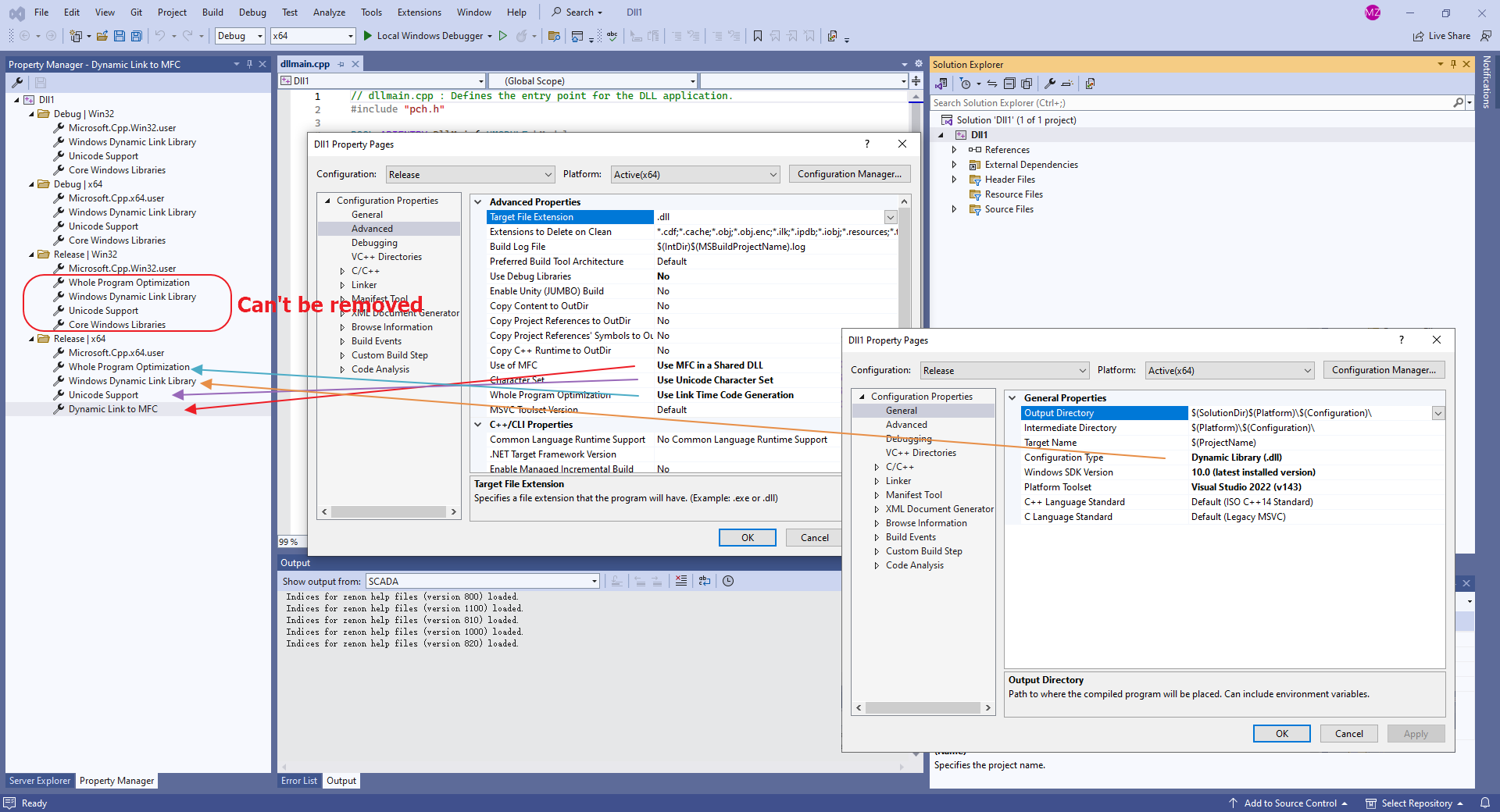
The problem with *.user files
Past versions of Visual Studio used global property sheets that had a .user file name extension and were located in the <userprofile>\AppData\Local\Microsoft\MSBuild\v4.0\ folder. We no longer recommend these files because they set properties for project configurations on a per-user, per-computer basis. Such “global” settings can interfere with builds, especially when you are targeting more than one platform on your build computer. For example, if you have both an MFC project and Windows Phone project, the .user properties would be invalid for one of them. Reusable property sheets are more flexible and more robust.
Although .user files are still installed by Visual Studio and participate in property inheritance, they’re empty by default. The best practice is to delete any reference to them in Property Manager to ensure that your projects operate independently of any per-user, per-computer settings. This practice is important to ensure correct behavior in a SCC (source code control) environment.
Share or reuse Visual Studio project settings
To create a custom group of settings that you can share with others or reuse in multiple projects, use Property Manager to create a property sheet (a .props file) to store the settings for each kind of project that you want to be able to reuse or share with others. Using property sheets are far less error-prone than other ways of creating “global” settings.
Macro
| Name | Description | |:———–|:———–| | ConfigurationName | 配置名字,通常是Debug或者Release | | IntDir | 编译器使用的中间目录,产出obj文件 | | OutDir | 链接器使用的输出目录 | | ProjectDir | 项目目录 | | ProjectName | 项目名字 | | SolutionDir | 解决方案目录 | | TargetDir | 目标输出文件所在的目录 | | TargetExt | 目标输出的扩展名 | | TargetFileName | 目标输出文件名,包括扩展名 | | TargetName | 目标输出名,不包括扩展名 | | TargetPath | 目标输出文件的全路径名 |
Post-Build Event
xcopy /y /d “....\MathLibrary$(IntDir)MathLibrary.dll” “$(OutDir)”
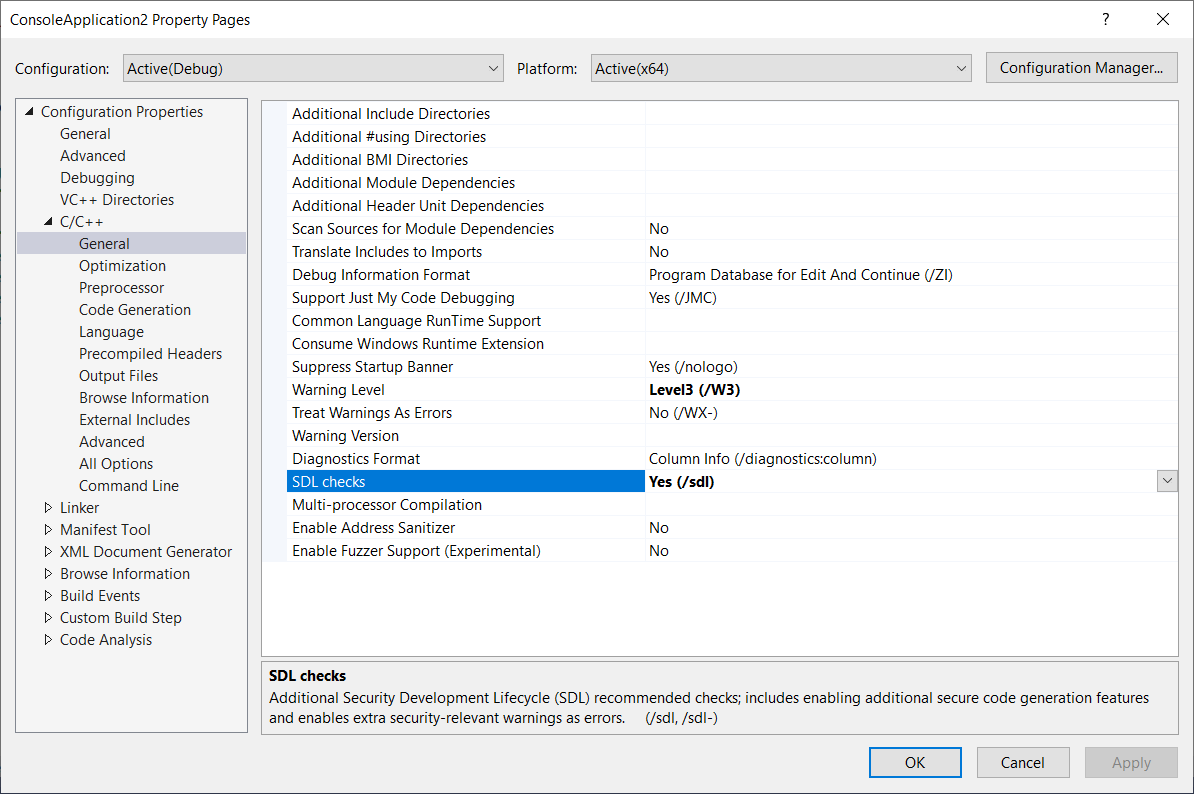
SDL Checks 启用附加安全检查
建议把改功能启用,该功能会把部分警告级别升级为错误级别,增加代码安全性。
MT MTd MD MDd
MT: multithread static MTDd: multithread deug static MD: multithread dynamic MDd: multithread dynamic debug