Binding
Selector.IsSynchronizedWithCurrentItem
- true if the SelectedItem is always synchronized with the current item in the ItemCollection;
- false if the SelectedItem is never synchronized with the current item;
-
null if the SelectedItem is synchronized with the current item only if the Selector uses a CollectionView. The default value is null.
//The following example binds two ListBox controls to the same ItemsSource. Because IsSynchronizedWithCurrentItem is set to true on each ListBox, the selected item is always the same for both controls <ListBox Name="employeeListBox1" ItemsSource="{Binding Source={StaticResource Employees}}" ItemTemplate="{StaticResource EmployeeItemTemplate}" IsSynchronizedWithCurrentItem="True"/> <ListBox Name="employeeListBox2" ItemsSource="{Binding Source={StaticResource Employees}}" ItemTemplate="{StaticResource EmployeeItemTemplate}" IsSynchronizedWithCurrentItem="True"/>
Binding.RelativeSource & BindingExpression.ResolvedSource
可以通过BindingExpression.ResolvedSource获取ResolvedSource对象,但是貌似每次通过Binding获取RelativeSource对象时,都是null。
BindingExpression.UpdateSource & UpdateTarget
手动更新绑定。
绑定源
WPF绑定一个控件是使用Binding.ElementName,绑定非控件对象时使用Source,RelativeSource,DataContext属性(WPF特有,而非XAML),只能绑定对象的公有字段。
- ElementName
- Source
- RelativeSource
- DataContext,如果没有使用Source或RelativeSource属性指定源,WPF就从当前元素开始在元素树中向上查找。检查每个元素的DataContext属性,并使用第一个非空的DataContext属性。UI元素树的每一个结点都有DataContext,当Binding只知道自己的path ,而不知道source时,会沿着 UI元素树一路的向树根部找过去,路过节点,比较结点的DataContext是否具有Path所指定的属性,有的话,把对应的节点对象作为自己的source
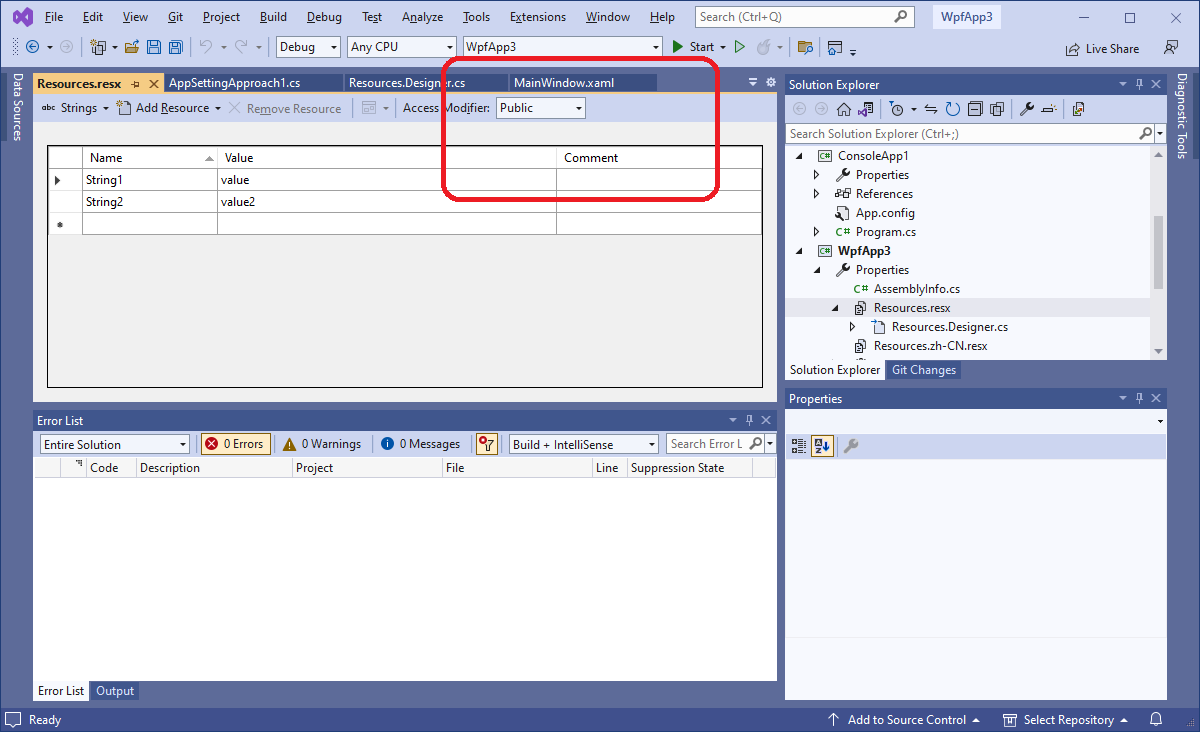
绑定到静态变量属性
可以在XAML文件中添加一个命名空间,然后绑定到该命名空间的类的静态属性上。要注意,绑定的静态属性的类必须为public,例如,当绑定到资源字符串上时,需要手动把资源设置为public。
xmlns:Properties="clr-namespace:WpfApp3.Properties"
<Button x:Name="btn_Static" Content="{Binding Path=(Properties:Resources.String1)}" />
<Button x:Name="btn_Static2" Content="{x:Static Properties:Resources.String1}" />
绑定在User Control的代码中定义的属性
ElementName=_this
<UserControl x:Class="SolutionExplorerUserControlLibrary.PMPPSolutionExplorerUserControl"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:SolutionExplorerUserControlLibrary"
mc:Ignorable="d"
d:DesignHeight="450" d:DesignWidth="800" Name="_this">
<Grid >
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"></RowDefinition>
<RowDefinition Height="*"></RowDefinition>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<TextBlock Text="{Binding ElementName=_this, Path=DataDirectory}"></TextBlock>
TargetNullValue
如果设置了该属性,当数据源具有null值时,将显示提供的值。
<TextBox x:Name="txtSpecification" Text="{Binding Product.Specification, TargetNullValue=[No Descripton Provided]}"></TextBox>
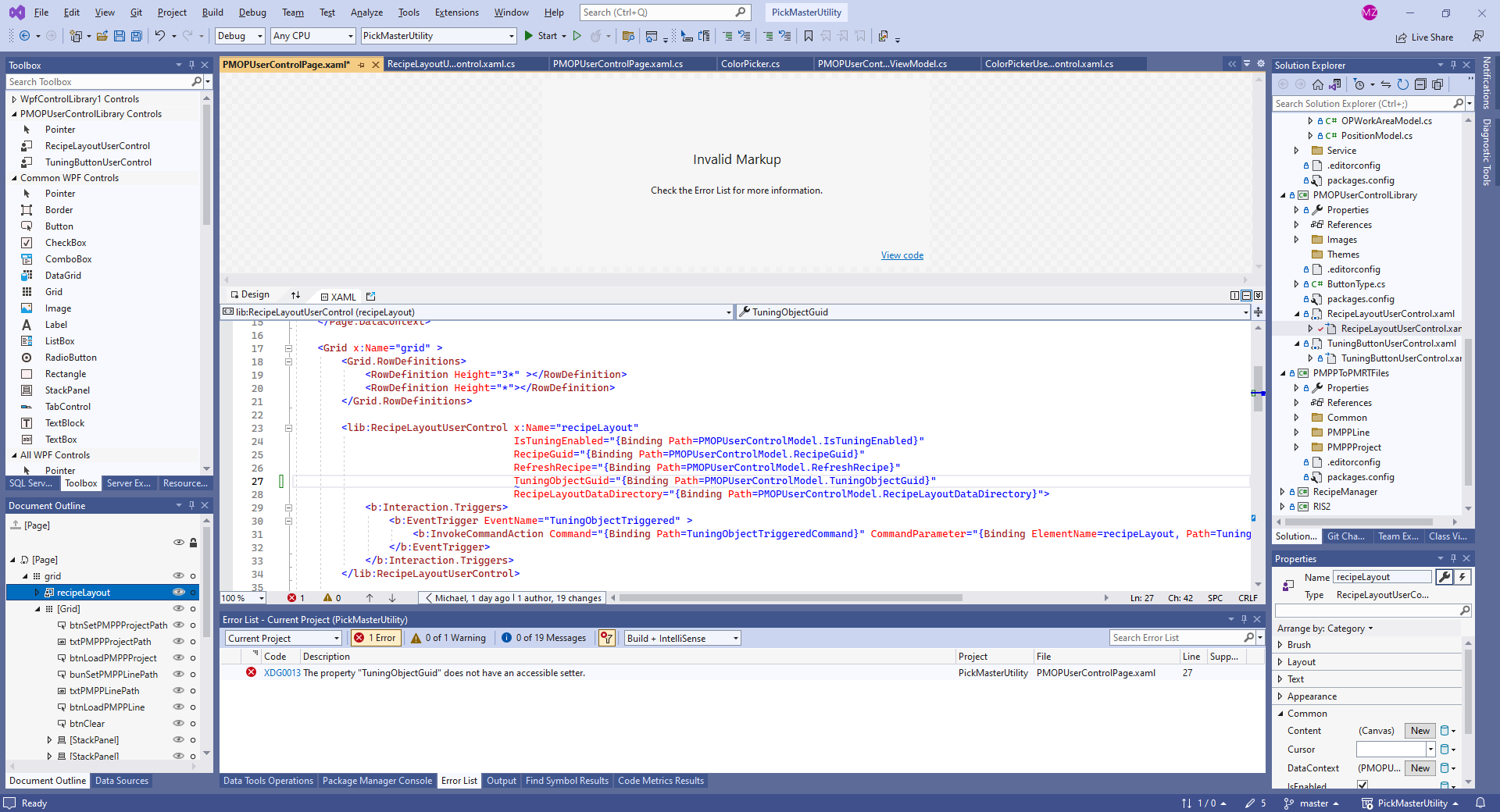
绑定目标属性
绑定目标属性必须为依赖属性,目标属性的setter可以为private,但此时貌似不能直接通过XAML设置,只能通过C#代码设置,且模式只能为OneWayToSource。推荐把依赖属性全部设置为public。
public static readonly DependencyProperty TuningObjectGuidProperty = DependencyProperty.Register("TuningObjectGuid", typeof(string), typeof(RecipeLayoutUserControl), new FrameworkPropertyMetadata(Guid.Empty.ToString()));
public string TuningObjectGuid
{
get => (string)GetValue(TuningObjectGuidProperty);
private set => SetValue(TuningObjectGuidProperty, value); // private accessible setter
}
//Right code
Binding binding = new Binding();
binding.Mode = BindingMode.OneWayToSource;
binding.Path = new PropertyPath("PMOPUserControlModel.TuningObjectGuid");
BindingOperations.SetBinding(this.recipeLayout, RecipeLayoutUserControl.TuningObjectGuidProperty, binding);
//Wrong code
<lib:RecipeLayoutUserControl x:Name="recipeLayout"
TuningObjectGuid="{Binding Path=PMOPUserControlModel.TuningObjectGuid}" >
验证
当验证失败时,每个控件都有一个附加属性System.Windows.Controls.Validation,记录验证错误。
if (Validation.GetHasError(productWindow.txtTotalProductQuantity))
{
MessageBox.Show("error");
}
验证数据错误方法一: ExceptionValidationRule, 通过数据对象中引发异常实现
如果绑定中没有设置ExceptionValidationRule,那么绑定源引发的异常会被WPF直接忽略掉,文本框不会有任何变化或提示。当设置了ExceptionValidationRule,下述代码中Exception(“xyz”)会被WPF捕获,此时WPF的文本框会出现红色框线,代表数据出错。
<TextBox x:Name="txtMyProperty">
<TextBox.Text>
<Binding Path="MyProperty">
<Binding.ValidationRules>
<ExceptionValidationRule></ExceptionValidationRule>
</Binding.ValidationRules>
</Binding>
</TextBox.Text>
</TextBox>
private int myVar;
public int MyProperty
{
get { return myVar; }
set {
if (value > 100)
{
throw new Exception("xyz");
}
myVar = value;
}
}
验证数据错误方法二: INotifyDataErrorInfo, 通过数据对象实现INotifyDataErrorInfo接口实现
WPF会自动检测绑定类有没有实现INotifyDataErrorInfo接口,如果实现了该接口,同样也会使用WPF控件通过视觉外观提示验证错误。此时需要确保绑定属性ValidatesOnNotifyDataErrors=True,True为默认值。
private int myVar;
public int MyProperty
{
get { return myVar; }
set
{
if (value > 100)
{
List<string> errors = new List<string>();
errors.Add("xyz");
SetErrors(nameof(MyProperty), errors);
}
else
{
ClearErrors(nameof(MyProperty));
}
myVar = value;
}
}
public event EventHandler<DataErrorsChangedEventArgs> ErrorsChanged;
private Dictionary<string, List<string>> errors = new Dictionary<string, List<string>>();
public bool HasErrors => errors.Count > 0;
public IEnumerable GetErrors(string propertyName)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(propertyName))
{
return errors.Values;
}
else
{
if (errors.ContainsKey(propertyName))
{
return errors[propertyName];
}
else
{
return null;
}
}
}
private void SetErrors(string propertyName, List<string> propertyErrors)
{
errors.Remove(propertyName);
errors.Add(propertyName, propertyErrors);
if (ErrorsChanged != null)
{
ErrorsChanged(this, new DataErrorsChangedEventArgs(propertyName));
}
}
private void ClearErrors(string propertyName)
{
errors.Remove(propertyName);
if (ErrorsChanged != null)
{
ErrorsChanged(this, new DataErrorsChangedEventArgs(propertyName));
}
}
验证数据方法三: 自定义验证规则ValidationRule
需要编写继承自ValidationRule的类,并添加到Binding.ValidationRules中,WPF会按顺序执行Binding.ValidationRules中的验证规格。
响应验证错误
通过设置Binding.NotifyOnValidationError为True,可以引发Error事件,该设置默认为False。Error事件为冒泡事件,所以可以在父控件中设置。
<Grid Validation.Error= "validationError">
<StackPanel >
<Label >test</Label>
<TextBox x:Name="txtTest" Text="{Binding MyProperty, NotifyOnValidationError=True}" ></TextBox>
</StackPanel>
</Grid>
private void validationError(object sender, ValidationErrorEventArgs e)
{
if (e.Action == ValidationErrorEventAction.Added)
{
MessageBox.Show(e.Error.ErrorContent.ToString());
}
}
窗口关闭前验证数据是否合法
public void ExecuteOK(System.Windows.Window window)
{
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
GetErrors(sb, window);
string errorMessage = sb.ToString();
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(errorMessage))
{
MessageBox.Show(errorMessage);
}
else
{
window.DialogResult = true;
window.Close();
}
}
private void GetErrors(StringBuilder sb, DependencyObject obj)
{
var s = LogicalTreeHelper.GetChildren(obj);
foreach (object child in LogicalTreeHelper.GetChildren(obj))
{
if (child is DependencyObject)
{
TextBox element = child as TextBox;
if (element != null && Validation.GetHasError(element))
{
sb.Append(element.Text + " has errors:\r\n");
foreach (ValidationError error in Validation.GetErrors(element))
{
sb.Append("\t" + error.ErrorContent.ToString());
sb.Append("\r\n");
}
sb.Append("\r\n");
}
GetErrors(sb, (DependencyObject)child);
}
}
}
路由事件绑定命令
<lib:RecipeLayoutUserControl x:Name="recipeLayout" IsTuningEnabled="{Binding Path=PMOPUserControlModel.IsTuningEnabled}" RecipeGuid="{Binding Path=PMOPUserControlModel.RecipeGuid}" RefreshRecipe="{Binding Path=PMOPUserControlModel.RefreshRecipe}">
<b:Interaction.Triggers>
<b:EventTrigger EventName="TuningObjectTriggered" >
<b:InvokeCommandAction Command="{Binding Path=TuningObjectTriggeredCommand}" CommandParameter="{Binding ElementName=recipeLayout, Path=TuningObjectGuid}"></b:InvokeCommandAction>
</b:EventTrigger>
</b:Interaction.Triggers>
</lib:RecipeLayoutUserControl>
代码设定Binding
//可以在创建Binding对象时,直接初始化源对象的path属性
Binding binding1 = new Binding("MyProperty");
binding1.Source = this;
//如果创建Binding对象时,没有初始化源对象的path属性,那么需要手动设置Binding对的Path属性
//binding1.Path = new PropertyPath("MyProperty");
BindingOperations.SetBinding(this.Text1, TextBlock.TextProperty, binding1);
//this.Text1.SetBinding(TextBlock.TextProperty, binding1);
代码设置XML的Binding
When the binding source is XML data instead of a common language runtime (CLR) object, the XPath property is used instead of the Path property to indicate the path to the value on the binding source to use.
XmlDocument xmlDocument = new XmlDocument();
xmlDocument.LoadXml(strXML);
XmlDataProvider xmlDataProvider = new XmlDataProvider();
xmlDataProvider.Document= xmlDocument;
xmlDataProvider.XPath = "Inventory/Books"; //使用XPath生成集合
Binding binding=new Binding("");
binding.Source = xmlDataProvider;
binding.XPath = "*[@Stock='out'] | *[@Number>=8 or @Number=3]";
BindingOperations.SetBinding(this.listTest, ListBox.ItemsSourceProperty, binding);